Overview
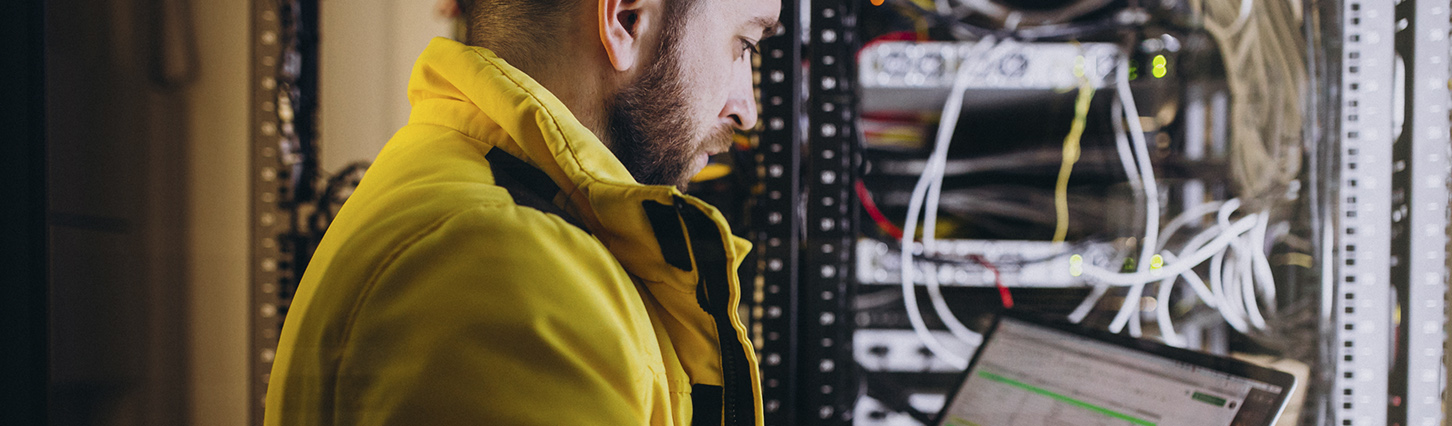
Infrastructure Solutions depends on combining various IT concepts to serve specific usage scenarios. our experience in the market enabled us to offer the best value-added infrastructure Solution in cooperation with the global IT Leaders.
IP Storage and Big Data Networking Solutions
The networking demands of big data analytics, flash-based and scale out storage, and hyper-converged compute solutions are driving a migration from legacy fiber channel to next generation IP-based storage networks. These next generation storage applications require an open, programmable, lossless and highly available IP storage networking solution in order to support their unique traffic patterns.
Arista's key benefits for Big Data acquisition and analysis include:
-Familiar GUI-based network administration tools for storage admins
-Return on Investment - Low power consumption, compact form factors
-Seamless migration to 25GbE and 50GbE for next generation IP Storage
SDN Automation and Orchestration (Cloud Control)
Contrail Cloud Platform releases are aligned with OpenStack community releases to maintain API compatibility and strong community support. Automated resource provisioning for configuration and operation of computing, storage, and networking resources needed by cloud applications minimizes manual intervention and improves operational
The attributes of Cloud Networking: Scalable, Low Latency, Open APIs, Programmable Management, Self-Healing Resiliency.
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an umbrella term encompassing several kinds of network technology aimed at making the network as agile and flexible as the virtualized server and storage infrastructure of the modern data center.The goal of SDN is to allow network engineers and administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements.
For enterprises,
Contrail Networking interoperates with OpenStack cloud orchestration
platform to enable system-level automation and orchestration. It reduces
the friction of migrating to cloud architectures by providing a
virtualized networking layer that seamlessly delivers switching,
routing, and networking services (security, load balancing, VPNs, etc.)
over an existing physical network. It also provides API compatibility
with public clouds like Amazon Web Services (AWS) for seamless workload
provisioning in hybrid environments.
For service providers,
Contrail Networking automates network resource provisioning and
orchestration to dynamically create highly scalable virtual networks and
to chain a rich set of Juniper or third-party virtualized network
functions (VNFs) and physical network functions (PNFs) to form
differentiated service chains on demand. Integrated with a cloud
management platform such as OpenStack, Contrail Networking enables the
agile creation and dynamic scaling of service instances with high
availability and reliability. Contrail Networking also makes it really
simple to onboard network functions onto the platform without requiring
any API integration or modifications to third-party service software.
Key Features
Switching and Routing: Hypervisor
forwarding plane provides line-rate routing and switching in a
multitenant virtualized environment that is completely decoupled from
the underlying physical fabric switches.
Load Balancing: Load
balancing is built right into the hypervisor’s forwarding plane for
balancing traffic across application tiers or network services.
Security and Multitenancy: The
use of L3VPN to create virtual networks inherently provides a secure
multitenant environment, where virtual networks cannot talk to each
other without policies. The Contrail Networking vRouter has built-in
distributed firewall capabilities that allow users to define security
policies between virtual networks. The security policies can specify
additional virtualized network services such as the Juniper Networks
Firefly Perimeter application-aware firewall; and distributed threat
prevention using Juniper Networks WebApp Secure, which can be spun up
between virtual networks.
Elastic, Resilient VPN: L3VPN, E-VPN, and site-to-site IPsec are all delivered in software.
Gateway Services: Contrail
interoperates with most routing equipment that supports L3VPN or E-VPN
with the appropriate data encapsulation standards, including Juniper
Networks MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers to seamlessly connect to
legacy workloads and non-virtualized physical services.
High Availability: All
Contrail Networking components are made highly available and offer
active/active redundancy. Each Contrail Networking VRouter is connected
to a set of control planes and gets the same routing table and access
control lists (ACLs).
Analytics Services: Rich
visualization and diagnostics of virtualized and physical networks
enable real-time and historical infrastructure analytics that can be
consumed through RESTful APIs. Users can also view live packet capture
of traffic between virtual networks.
API Services: RESTful
API for configuration, operation, and analytics provides seamless
integration with OpenStack or service provider OSS/BSS systems. This
includes Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) API compatibility for seamless
deployment of applications in a hybrid environment (e.g., private cloud
and public cloud/AWS).
Cloud Enabled Enterprise
The attributes of Cloud Networking : Scalable, Low Latency, Open APIs,
Programmable Management, Self-Healing Resiliency. software-defined
networking (SDN) Software-defined networking (SDN) is an umbrella term
encompassing several kinds of network technology aimed at making the
network as agile and flexible as the virtualized server and storage
infrastructure of the modern data center. The goal of SDN is to allow
network engineers and administrators to respond quickly to changing
business requirements.
SDN Benefits:
1.Centralized network provisioning
Software
defined networks provide a centralized view of the entire network,
making it easier to centralize enterprise management and provisioning.
For example, more VLANs are becoming part of physical LANs, creating a
Gordian knot of links and dependencies. By abstracting the control and
data planes, SDN can accelerate service delivery and provide more
agility in provisioning both virtual and physical network devices from a
central location.
2.Holistic enterprise management
Enterprise
networks have to set up new applications and virtual machines on demand
to accommodate new processing requests such as those for big data. SDN
allows IT managers to experiment with network configuration without
impacting the network. SDN also supports management of both physical and
virtual switches and network devices from a central controller;
something you can’t do with SNMP. SDN provides a single set of APIs to
create a single management console for physical and virtual devices.
3.More granular security
One
of the advantages of security defined networking that appeals most to
IT managers is centralized security. Virtualization has made network
management more challenging. With virtual machines coming and going as
part of physical systems, it’s more difficult to consistently apply
firewall and content filtering polices. When you add in complexities
such as securing BYOD devices, the security problem is compounded.
The
SDN Controller provides a central point of control to distribute
security and policy information consistently throughout the enterprise.
Centralizing security control into one entity, like the SDN Controller,
has the disadvantage of creating a central point of attack, but SDN can
effectively be used to manage security throughout the enterprise if it
is implemented securely and properly.
4.Lower operating costs
Administrative
efficiency, improvements in server utilization, better control of
virtualization, and other benefits should result in operational savings.
Although it is still early to show real proof of savings, SDN should
lower overall operating costs and result in administrative savings since
many of the routine network administration issues can be centralized
and automated.
5.Hardware savings and reduced capital expenditures
Adopting
SDN also gives new life to existing network devices. SDN makes it
easier to optimize commoditized hardware. Existing hardware can be
repurposed using instructions from the SDN controller and less expensive
hardware can be deployed to greater effect since new devices
essentially become “white box” switches with all the intelligence
centered at the SDN controller.
6.Cloud abstraction
Cloud
computing is here to stay and it is evolving into a unified
infrastructure. By abstracting cloud resources using software defined
networking, it’s easier to unify cloud resources. The networking
components that make up massive data center platforms can all be managed
from the SDN controller.
7.Guaranteed content delivery
The
ability to shape and control data traffic is one of the primary
advantages of software defined networking. Being able to direct and
automate data traffic makes it easier to implement quality of services
(QoS) for voice over IP and multimedia transmissions. Streaming high
quality video is easier because SDN improves network responsiveness to
ensure a flawless user experience.
The specific advantages of
software defined networking will vary from network to network, but there
are benefits from network abstraction and the agility it offers for
network administration and automation. The best way to get the most out
of SDN is to assess the network components and infrastructure to
determine if SDN can help address issues such as resource availability,
virtualization, and network security. Software defined networking isn’t
the right approach for every network environment, but when there are
clear benefits, SDN could be just the solution you need to optimize your
data center.
SD-WAN
Software-defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) product provides a virtual WAN architecture that allows enterprises to leverage any combination of transport services – including MPLS, LTE and broadband internet services – to securely connect users to applications.
An SD-WAN uses a centralized control function to securely and intelligently direct traffic across the WAN. This increases application performance, resulting in enhanced user experience, increased business productivity, and reduced costs for IT.
Application Delivery Control
Application Delivery Controller products provide load balancing, application acceleration, web application firewall, SSL termination, and security along with seamless access to applications. ADCs, also called app delivery controllers, may be delivered in three form factors: hardware appliances, virtual appliances (the software extracted from legacy hardware) and software-only load balancers.